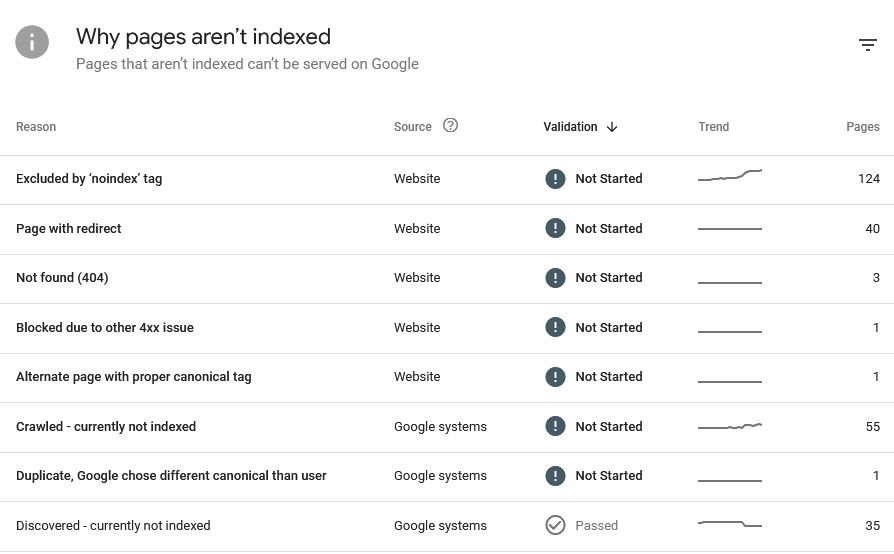
Understanding the “Crawled Currently Not Indexed” Problem
When Google Search Console shows crawled currently not indexed, it means Googlebot has visited your page, processed it and added it to its crawl queue, but chose not to index it. This is extremely common for both new and established websites, and it affects SEO visibility, organic traffic and site authority.
Although crawled currently not indexed doesn’t necessarily indicate a penalty, it is a signal that Google does not yet trust the page enough to include it in search results. This could be related to content quality, duplication, thin pages, slow performance, poor E-E-A-T, or technical errors.
Before fixing the issue, it’s essential to understand how Google evaluates pages and why so many URLs fall into this category.
Why Google Marks Pages as “Crawled Currently Not Indexed”
1. The Content Isn’t Strong Enough
Google wants authoritative, useful content. If your page provides little value, repeats other pages, or isn’t comprehensive, it often becomes crawled currently not indexed.
Thin content and doorway pages frequently fall into this category.
2. The Page Is Too Similar to Another URL
Duplicate content is one of the biggest triggers.
Related GSC statuses include:
- Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical
- Alternate page with proper canonical tag
Google may crawl both URLs but only index the strongest one, leaving the other crawled currently not indexed.
3. The Page Was Discovered but Lacks Importance
If Google sees a page as low value, it may label it:
- Discovered – not indexed
This often precedes crawled currently not indexed. New websites and large e-commerce catalogues experience this frequently.
4. Technical Blocks or Conflicts
Even if a page is crawled currently not indexed, technical problems can still be involved.
Common issues include:
- Blocked by robots.txt
- Crawled – but blocked by robots.txt
- Soft 404 (Not Found)
- Noindex meta tags
- Server errors or slow response times
These can confuse Google, leading to limited indexing.
5. Poor Internal Linking Structure
If Googlebot struggles to find or understand the importance of a page, it might crawl it but not index it.
Pages with:
- No internal links
- Hidden navigation
- Orphaned content
…routinely end up crawled currently not indexed.
6. Lack of External Signals
Backlinks and brand mentions help Google assess the value of a page. Without them, the page may remain in the queue for months.
How to Fix “Crawled Currently Not Indexed” Step by Step
1. Improve On-Page Content Quality
Your content must demonstrate:
- Expertise
- Experience
- Authority
- Trust
Tips:
- Expand the content depth
- Add unique insights
- Include supporting visuals
- Improve formatting and readability
- Add FAQs for search intent
Pages that deliver real value rarely remain crawled currently not indexed for long.
2. Resolve Duplicate Content Issues
If Google detects duplication, it may choose to index only the “main” version and leave the other crawled currently not indexed.
Fixes:
- Use consistent canonical tags
- Consolidate similar pages
- Remove thin duplicate URLs
- Rewrite product descriptions
- Avoid using manufacturer descriptions across thousands of products
When Google sees each page as unique, indexing increases significantly.
3. Check for Robots.txt and Noindex Problems
Many sites accidentally block pages.
Review:
- robots.txt for disallowed paths
- meta noindex in source code
- X-Robots-Tag headers
- Crawled – but blocked by robots.txt warnings
If a page is accidentally disallowed, it may appear crawled currently not indexed and never enter the search index.
4. Fix Soft 404 and Broken Elements
Google marks pages as soft 404 when:
- The content is too thin
- The page appears empty
- The page lacks value
- The template loads but the content doesn’t
Solving these issues ensures the page is seen as legitimate, preventing the crawled currently not indexed status from sticking.
5. Strengthen Internal Linking
A robust internal linking structure tells Google which pages matter.
Recommendations:
- Add internal links from high-authority pages
- Include links in your homepage or category pages
- Use descriptive anchor text
- Create topic clusters
This increases crawl priority and helps Google index previously ignored content.
6. Improve Page Speed and Technical Health
Slow pages or unstable hosting can cause indexing issues.
Optimise:
- Core Web Vitals
- Image compression
- Server response times
- JavaScript rendering
- Mobile performance
A technically strong page is less likely to remain crawled currently not indexed for long.
7. Build High-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks increase trust and authority. When pages gain links, Google often re-evaluates them and removes the crawled currently not indexed status.
Ideas:
- Digital PR campaigns
- Guest posting
- Resource link building
- Broken link outreach
Even a few high-authority links can make a dramatic difference.
8. Use the URL Inspection Tool for Re-Indexing
Once your improvements are complete, request re-indexing through Search Console.
This prompts Google to revisit the page faster, helping move it from crawled currently not indexed into the index.
How to Prevent “Crawled Currently Not Indexed” in the Future
Prevention is easier than fixing.
1. Maintain a Clean Crawl Budget
Large websites must prioritise:
- Removing outdated pages
- Avoiding endless pagination
- Preventing thin auto-generated content
Google prefers crawling important URLs.
2. Only Publish High-Quality Material
Google’s quality bar increases yearly. Thin or rushed content often ends up crawled currently not indexed immediately.
3. Keep Your Sitemap Fresh and Accurate
Remove dead URLs and include only index-worthy pages.
4. Build Topical Authority
When Google trusts your niche expertise, indexing improves automatically.
5. Monitor Search Console Weekly
Catch issues like:
- Discovered – not indexed
- Soft 404
- Duplicate content alerts
- Blocked by robots.txt
Early fixes prevent indexing delays.
All in all!
Pages marked crawled currently not indexed are not lost causes—they simply require improvement, clarity and stronger signals of value. By enhancing content quality, resolving duplication, fixing technical barriers, boosting internal linking and improving authority, you can move these URLs into Google’s index and regain organic visibility.
If you manage your site consistently and monitor indexing issues, you’ll significantly reduce the chances of seeing crawled currently not indexed or related errors like Discovered – not indexed, Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical, Soft 404, or Blocked by robots.txt in the future.







